Diseases
Astigmatism

Definition
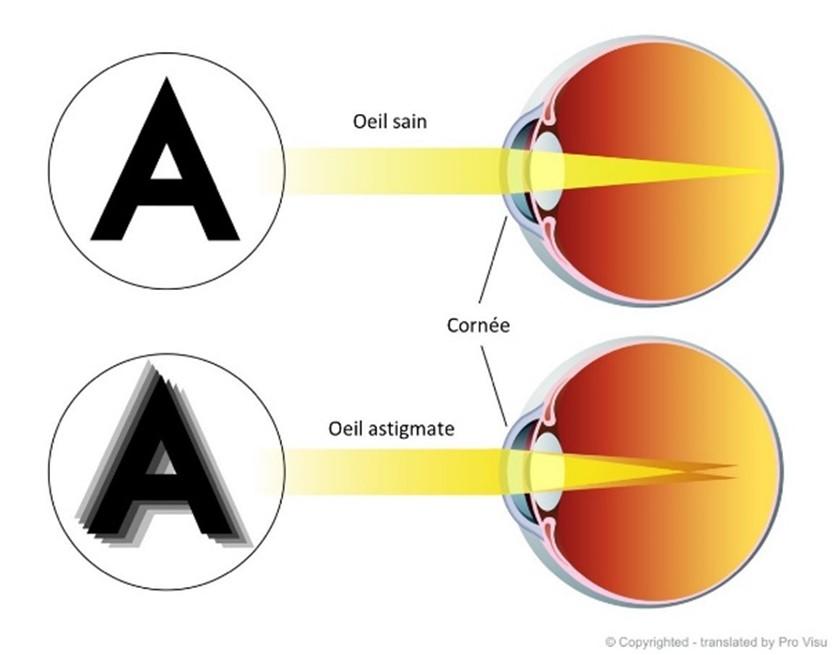
Astigmatism is a refractive disorder caused by an irregularity in the curvature of the cornea (the structure covering the front surface of the eye) or the crystalline lens (the lens behind the iris). This irregularity results in blurred or distorted vision. Astigmatism is often associated with other refractive disorders such as myopia or hyperopia.
Causes
Astigmatism can be hereditary or acquired:
- Hereditary astigmatism is most often regular (deformation of the curvature along a single axis). This type of astigmatism is easier to correct.
- Acquired astigmatism is most often irregular (irregular deformation of the curvature) and may be due to scarring of the cornea following injury or surgery.
Astigmatism can also be linked to keratoconus (irregular cone-shaped deformation of the cornea).
Symptoms
The main symptom of astigmatism is blurred or distorted vision at any distance. Headaches and eye strain can also be associated with astigmatism.
Diagnosis
There are several tests to diagnose astigmatism:
- Measurement of visual acuity
- Refraction measurement
- A complete eye examination
The degree of astigmatism is expressed in diopters: weak between 0 and 1 diopter, moderate between 1 and 2 diopters, and strong above 2 diopters.
It's important to carry out these examinations in children to avoid any visual problems interfering with learning.
Treatments
Low-dioptre astigmatism does not necessarily require treatment. Above 1 diopter, it is mainly corrected by wearing glasses or adapted contact lenses.
Laser surgery, performed on an outpatient basis under local anaesthetic, is also available. In most cases, patients no longer need to wear corrective lenses. However, the presence of keratoconus is a contraindication to the procedure.
Like all surgery, laser surgery carries the risk of complications such as infection, dry eye and glaucoma.
Frequency
The majority of people have astigmatism, as it's rare to have a perfectly round cornea and lens. However, clinically significant astigmatism (diopter of at least 0.5) affects between 25% and 30% of the population. This prevalence increases with age.
References
Astigmatisme - Fondation Asile des aveugles (ophtalmique.ch)
Astigmatisme | The Canadian Association of Optometrists
Vision floue - Troubles oculaires - Manuels MSD pour le grand public (msdmanuals.com)
Contenu revu et contrôlé le 27.04.2023.