Diseases
Hordeolum
A benign bacterial infection
Synonym(s)
Compère-loriot - Hordeolum
Definition
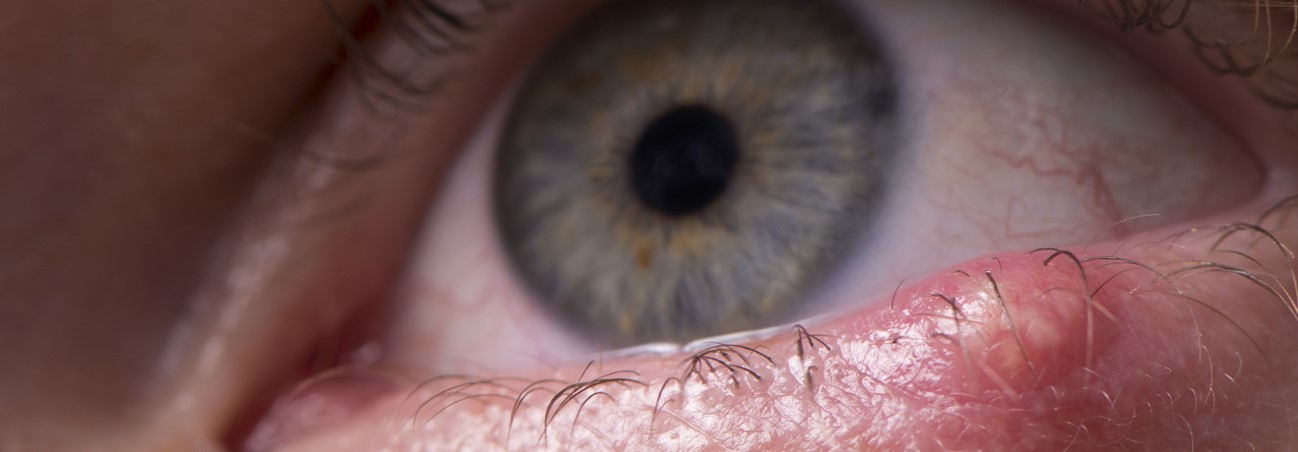
A stye is a benign bacterial infection at the root of an eyelash, most often caused by staphylococcus. It usually begins with redness at the edge of the eyelid, causing pain and itching. Pus gradually accumulates at the root of the eyelash, causing a painful swelling with a yellowish spot at its center, often giving the affected person the impression of having a foreign body under the eyelid. The eye is sensitive to light and watery. The stye usually breaks spontaneously within a few days, releasing the pus and disappearing on its own. However, recurrence is not uncommon.
Occasionally, the stye may develop internally, causing pain and symptoms that are often more severe than in the case of an external stye, since the swelling develops under the eyelid. When the inflammation is serious, it may be accompanied by fever or a cold.
Risk factors
People with diabetes, dry eyes, seborrheic dermatitis or immune deficiency are at greater risk of developing styes. This is also the case for contact lens wearers, especially when hygiene standards (e.g. hand washing) are not scrupulously respected.
Prevent
It's important to maintain good eye hygiene:
- Avoid rubbing your eyes with your fingers, and use the back of your hand to avoid introducing bacteria.
- Remove make-up every night with non-irritating products, and don't lend your make-up equipment.
- Respect hygiene rules when wearing contact lenses.
- Wear goggles or a diving mask in swimming pools.
Styes usually rupture spontaneously within a few days, releasing the pus and disappearing on their own.
Treatment
A stye usually heals spontaneously within a week. Warm compresses can be applied to the affected eye to relieve pain and promote maturation, rupture and spontaneous drainage of the stye. If the stye persists despite the correct application of warm compresses, a doctor may need to pierce it. In some cases, antibiotics applied directly to the eye may be prescribed. These are of limited help, however, as most styes disappear on their own. For more severe eye infections, oral antibiotics may be required.
In the case of an internal stye, healing is rarely spontaneous, and surgical drainage is often necessary. In this case, oral antibiotics are prescribed after the operation.
Frequency
Stye is an extremely common pathology, with obvious and painful symptoms.
References
content reviewed and controlled on 16.01.2025